Working with Multimedia
-Consider bandwidth when working with multimedia on a Web site
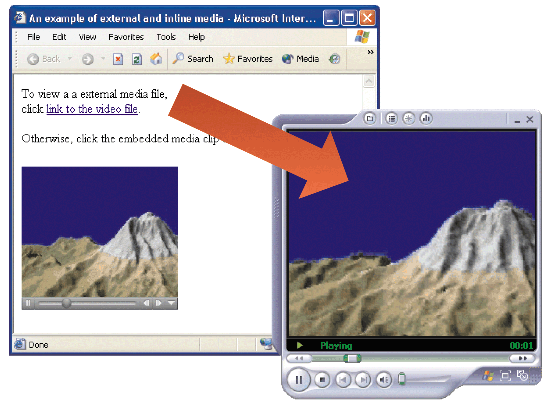
-External media is a sound of video file that’s accessed through a link.
~Useful for a low bandwidth
-Inline media is placed within a Web page as an embedded object
Working with Audio
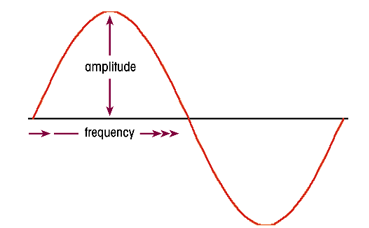
-Amplitude- the height of the wave. Amplitude relates to the sound’s volume (the higher the amplitude, the louder the sound).
-Frequency- the speed at which the sound wave moves. Frequency relates to sound pitch (high frequencies have high pitches).
Sampling Rate, Sample Resolution, and Channels
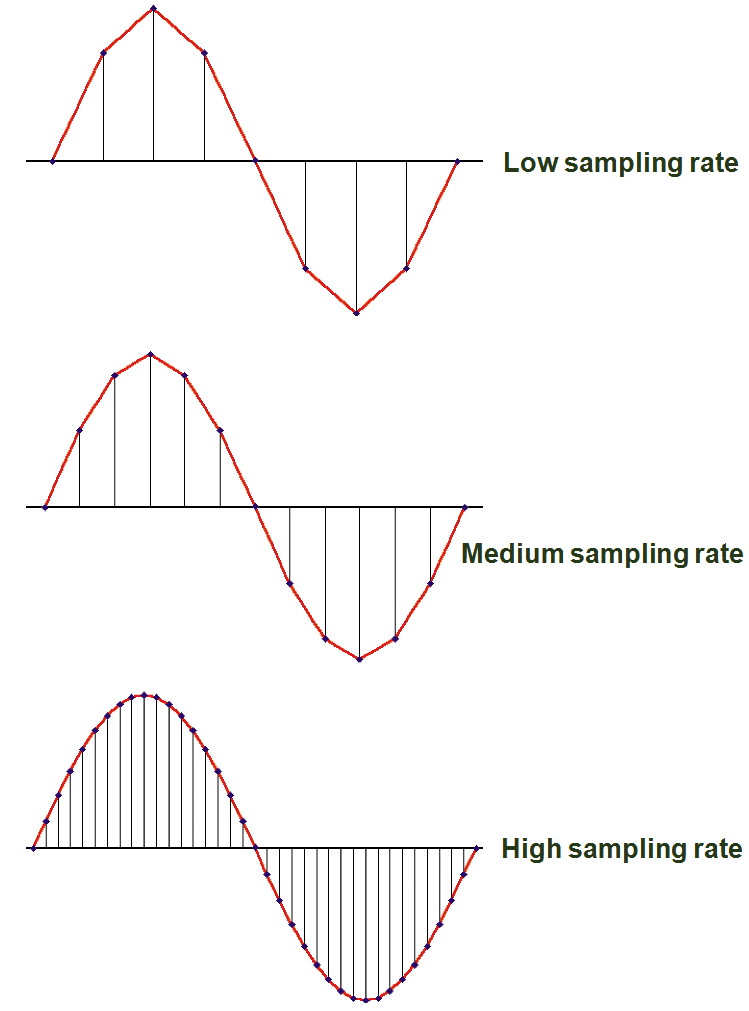
-To store the information, however, it must be converted to pieces of information
-Each measurement is called a sample.
~Samples per second taken is called the sampling rate
Sampling Rate
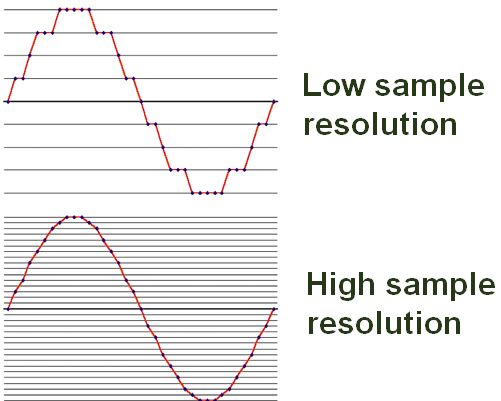
-8-bit
-16-bit
-32-bit
Sample Resolution
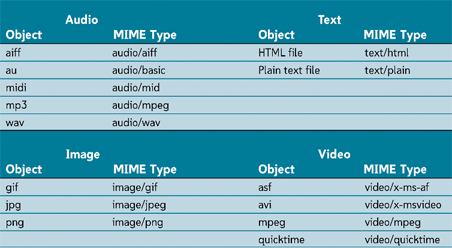
Sound File Formats
Linking to an Audio Clip
Inserting links to the sound clips

Embedding an Audio Clip
-Browsers need the appropriate plug-ins to run embedded objects
Playing Background Sounds
<bgsound src=“url” balance=“value”
loop=“value” volume=“value” />
Working with Video
Frame Rates and Codecs
-This is one way to control file size of video files
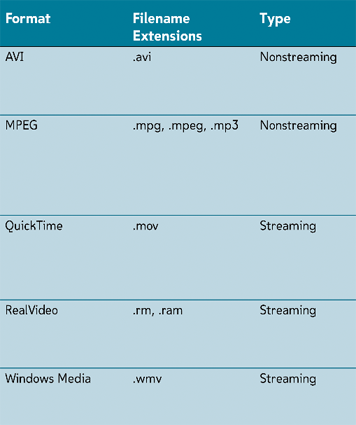
Video File Formats
Linking to a Video Clip
Embedding a Video Clip
Using a Dynamic Source
<img src=“url” dynsrc=“url” start=“type”
loop=“value” control=“control” />
Where the dynsrc attribute specifies the URL of a dynamic (video) version of the inline image. The start attribute tells the browser when to start the clip, the loop attribute specifies the number of times the video will play, and the control attribute specifies whether IE should display player controls below the inline image to start and stop the video clip
Supporting Non-Embedded Elements/p>
<embed attributes />
<noembed>
alternate content
</noembed>
where alternate content is the content displayed by browsers that don’t support embedded objects
Creating a Marquee with Internet Explorer
<marquee attributes>
content
</marquee>
Where attributes is one or more of the marquee elements, and content is the page content that appears in the marquee box.
Working with the Object Element
-Inline images
-Sound clips
-Video clips
-Program applets
-Other HTML documents
Specific and generic elements